
The Carpathians cover an area of about 209,000 km2 which is home a population of 17 million. The highest peak in the Carpathians is the Gerlach in Slovakia at 2,655 m. The Carpathian range extends from Austria to Serbia, covering most of Slovakia and Romania and parts of the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Ukraine. The Carpathians form a natural bridge between western and eastern Europe for species migration and genetic exchange. They contain some of the most intact ecosystems and are home to a wealth of indigenous species. The Carpathian landscape has largely been shaped by a long tradition of mountain agriculture and sheep farming. Today these traditional occupations are in decline because of economic development and increasing pressures on the natural environment. However, five Carpathian countries have now joined the European Union, which should increase the potential for sustainable development through new environmental policies.
Cooperation on conservation and between protected areas is becoming ever more essential. The network will respond to the need for cooperation and coordination – for example by facilitating thematic exchanges to identify key issues and creating joint instruments. The Carpathian Network of Protected Areas (CNPA) was created in December 2006 as a means of implementing the Carpathian Convention and has increased the potential for cooperation within the massif and with neighbouring mountain areas. |
|
Surface:
209,000 km2
Population:
17 million
Highest peak:
2,655 m
(Gerlachovský štít)
Countries:
Serbia, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Ukraine
Map:
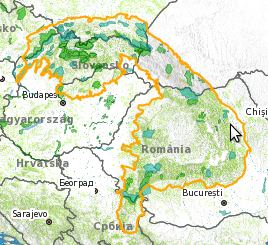
|
|
News
|







